Potassium iodate is an ionic compound that is made of K+ ion and IO3– ion in the ratio 1:1. It has a molecular formula KIO3. It is an oxidising agent and thus can cause when it comes in contact with combustible agents. It can be obtained by treating potassium hydroxide with iodic acid. In this short piece of article, let us learn more about the potassium iodate formula along with its chemical structure, properties and uses.
Potassium Iodate Properties
| Properties of Potassium Iodate | |
| Name | Potassium Iodate |
| Also Known as | Potassium Iodine Oxide, Iodic Acid, Potassium Salt |
| Appearance | White crystalline powder |
| Chemical Formula | KIO3 |
| Melting Point | 560 °C |
| Molar Mass | 214.001 g/mol |
| Density | 3.89 g/cm³ |
| Solubility in Water | Soluble |
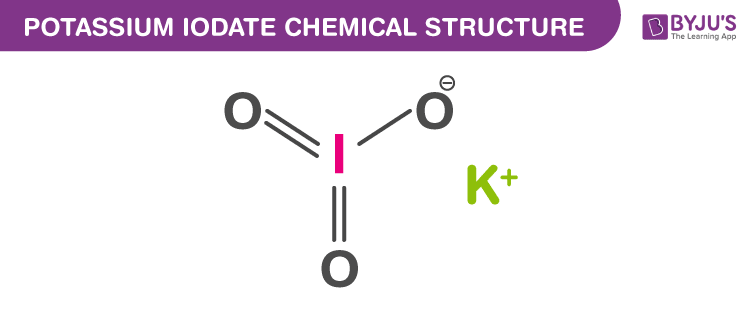
Potassium Iodate Structure
Potassium Iodate Uses
- Used in the iodination of table salt to prevent iodine deficiency
- Occasionally used as a maturing agent in baking
- Used to prevent the accumulation of radioactive iodine in thyroid
At BYJU’S, learn more formulas of different chemical compounds along with their chemical structure and properties.
Comments